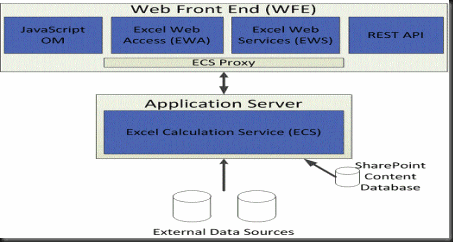
There are already tons of articles to help you out in setting up the PowerPivot, however each setup has its own set of challenges. In this article I am going to highlight the issues I faced and I am sure it can save someone that 1 week of time that I spent on it.
At the end of the article I will also publish a few references that helped me in my setup.
Claims based authentication is the only way to create your web application if you want to support Forms Authentication. i.e. any Authentication provider that is not tied to Active Directory (in which case you could chose your web application to be Classic mode)
If you are reading this article thinking that you can setup Power Pivot on your Claims based Web application, you would be sorry to hear that it is NOT supported. I learnt it the hard way.
You can still view the Power Pivot reports published without any trouble but, you will not be able to take the advantage of the Data Refresh (On Demand/Scheduled) capabilities of Power Pivot.
However, I was able to get it working on my laptop (DC, SP Server, DB & Analysis Server). But, with a limitation that I needed to be a Domain Admin & Farm Admin. It worked only through a unattended account which was tied to a Secure Store Service Application ID configured with the Domain Account.
The same did not work on a multi box environment. Not able to understand why? I was working with a Microsoft Tech support to resolve this though. Which I think now is futile.
For the installation problems, you can refer to my previous article:
Either you are setting up the PowerPivot on Claims/Classic based Web applicaiton, you will definitely want to take care of the following:
1. Ensure that you have deployed the PowerPivotFarm.wsp globally & PowerPivotWebApp.wsp for the Web Application you are enabling Power Pivot capabilities.
See Central Administration > System Settings > Farm Management > Manage Farm Solutions >
2. Ensure that Secure Store Service, SQL Server Analysis Services, SQL Server PowerPivot System Service, Timer Service are started.
See Central Administration > System Settings > Servers > Manage Services on Server
3. Few Features have to be activated in the Site collection.
PowerPivot Feature Integration for Site Collections
SharePoint Server Publishing Infrastructure
SharePoint Server Publishing
See, Site Settings > Site Collection Administration > Site Collection Features >
4. If you have changed the master page then you may end up failing to load the power pivot gallery. Add the following in the VirtualDirectory\{app port}\web.config
<SafeControl Src="~/_layouts/powerpivot/*" IncludeSubFolders="True" Safe="True" AllowRemoteDesigner="True" SafeAgainstScript="True" />
5. For data refresh ensure that the application pool account of the Power Pivot Service Application has enough privileges.
6. You may need to setup Kerberos (or enable for Delegation in Active Directory) when you have multiple box setup. This one I am not sure yet.:)
Some settings that you need to be aware of for the Power Pivot.
1. Creating Secure Store Service Application ID
2. Linking that in the Power Pivot Excel Workbook while publishing it. I may write another article very soon.
3. Central Administration > PowerPivot > Configure Service Application Settings
4. Central Administration > Monitoring > Timer Jobs > Review Job Definitions > PowerPivot Data Refresh Timer Job
References:
Hope this information was useful. Look forward for your experiences in setup.